Factsheets - Equine
Below are Word and PDF files of our Factsheets. You will need Adobe Reader to view the PDF files - if you need to download Adobe Reader please click here.
Please note: some of these factsheets are several pages long and are large files, so please be patient when downloading!
Sidebone
The term 'sidebone' describes a condition where calcium deposits are laid down within the lateral cartilages, in a process called mineralisation.
Steroids (Anti-Inflammatories)
Steroids are a type of pharmaceutical that can be divided in two general categories. The first are called corticosteroids, which are potent anti-inflammatories used for a range of conditions from lameness to intestinal and respiratory problems. The second include anabolic steroids which are used to stimulate muscle development and general weight gain. This factsheet covers the use of corticosteroids, which are similar synthetic versions of a natural hormone produced by the adrenal glands, next to the kidneys.
Strangles
Strangles is a very common but unpleasant bacterial disease that can affect horses, ponies and even donkeys. Signs vary between individuals and can range from very mild to dramatic in appearance. The disease is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus equi subspecies equi (Strep. equi) and is highly contagious being spread by direct contact with infected discharges or with contaminated clothing or equipment. Horses can be silent carriers of the bacteria displaying no outward signs but being capable of infecting others.
Surgical Colic
Colic is a term used to describe a range of conditions associated with the gastrointestinal tract which present as abdominal pain.
Colic can be classified into three general categories, including:
Medical colic, false colic and surgical colic.
Medical colic can be treated conservatively using drug therapies and other non-surgical means, without resorting to surgery. False colic refers to conditions which can appear similar to abdominal discomfort, but are conditions outside of the abdomen (e.g. tying up and laminitis).
Surgical colic refers to those cases of colic which require surgical correction under general anaesthesia. This fact sheet will focus on surgical colic.
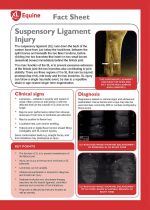
Suspensory Ligament Injury
The suspensory ligament (SL) runs down the back of the cannon bone from just below the hock/knee, between the splint bones and beneath the two flexor tendons, before dividing into two branches that insert on two small bones (sesamoid bones) immediately behind the fetlock joint.
The main function of the SL is to prevent excessive extension of the fetlock joint; the two branches also contributing to joint stability. There are three regions of the SL that can be injured; proximal (top end), mid-body and the two branches. SL injury can follow a single traumatic event, be due to a repetitive strain or age related longer term degeneration.
Sweet Itch
Sweet itch is a hypersensitivity reaction to the bite of a midge which produces skin irritation that leads to rubbing, scartching and biting of the affected areas resulting in hair loss and skin damage.
Tendon Injuries
Flexor tendon injuries are relatively common in horses. Superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT) injuries are particularly common in eventers and racehorses, but can occur in any horse through field injury or over-exertion. The primary defect is a central rupture of tendon fibres resulting in bleeding and swelling. A tendon injury need not be career ending as most are treatable, but prompt diagnosis and early, appropriate treatment can prevent catastrophic breakdown and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Tetanus
Tetanus or 'lockjaw' is an acute, usually fatal disease caused by a bacterium Clostridium tetani found in soil.
The Donkey's Foot
Donkeys are particularly prone to foot problems because in captivity in the UK they are managed in a damp environment with a temperate climate. They frequently have access to lush grazing, contrasting vastly with the desert conditions and fibrous diets where they evolved to survive and thrive in the wild. These differences increase the risk for the development of poor quality horn, laminitis and white line separation and disease.
The Dull Donkey
The donkey is very stoical in nature, which can make detection of sickness and disease very difficult. Dullness and depression are frequently the only symptoms exhibited for a number of conditions, including severe and life threatening illness. Donkeys are affected by many of the same conditions as horses, but may present in a different way e.g. colic presenting as dullness only. Any dull donkey should be promptly examined by a vet to prevent development of hyperlipaemia, a potentially fatal condition.