Factsheets - Equine
Below are Word and PDF files of our Factsheets. You will need Adobe Reader to view the PDF files - if you need to download Adobe Reader please click here.
Please note: some of these factsheets are several pages long and are large files, so please be patient when downloading!
The Growing Foal
A healthy foal will grow rapidly, gaining up to 90% of its adult height in the first two years of life. Getting a foal’s growth rate and development right during this time is essential for providing the foal with the best possible start for an athletic career.
There are many different factors that will affect a foal’s start in life, but the ones that we can control and manage include:
appropriate diet for age and stage of growth
de-worming
preventive vaccination program
farriery.
The Newborn Foal
After eleven months of waiting, when your bundle of joy finally arrives; it is worth knowing some facts about the newborn foal, especially about the first few hours of life.
The Rig
A rig is an entire male horse with no signs of external testicles so appears to be a gelding; but one or two testicles are still present, producing testosterone. A rig behaves like a stallion and, potentially, may be fertile. Their behaviour is unpredictable and they can be dangerous to handle so they should be castrated.
Some geldings still show stallion-like behaviour despite being fully castrated; they are called “false rigs”. The only form of treatment in these cases is behavioural therapy.
Tie Forward Surgery
Dorsal displacement of the soft palate (DDSP) is a performance-limiting condition of the upper respiratory tract which occurs during fast exercise when the soft palate moves above the epiglottis (part of the larynx), creating a functional obstruction within the airway. This restricts airflow to the lungs and causes a sudden loss of performance and often a choking or gurgling noise.
Tie-back and Hobday Surgery
A Tie-back and a Hobday are surgical procedures commonly performed together as treatment for recurrent laryngeal neuropathy (RLN), a condition causing paralysis of the nerve supplying the muscles of the larynx. This is the most common cause of abnormal respiratory noise in exercising horses and is often referred to as ‘whistling’ or ‘roaring’. It almost exclusively occurs in large horses, primarily Thoroughbreds and Warmbloods
Tooth Extraction
Dental problems such as tooth root abscesses, fractured teeth and periodontal disease will commonly require dental extraction as part of the treatment protocol.
Dental extraction can be a time consuming and difficult process (even when the teeth feel loose!) and requires a wide range of surgical equipment. Dental extraction should only be carried out by a veterinary surgeon with experience in dental surgery.
Tuberculosis - A concern for all animals
bTB is caused by Mycobacterium bovis, a bacteria that can infect many different animals. It is spread either by inhaling or consuming the bacteria and is usually associated with animals living in enclosed spaces. It can also be spread through contaminated surfaces such as feed troughs and pasture. The disease causes weight loss, coughing, fever, lethargy and ultimately, death.
Urticaria
Urticaria is one of the most commonly encountered skin diseases in horses. It is an allergic reaction manifested in the appearance of soft raised skin nodules or plaques.
Vaccinations against Influenza and Tetanus
Vaccinations protect your horse against life-threatening diseases such as tetanus, and diseases that can severely affect their health and performance, such as equine influenza (flu).
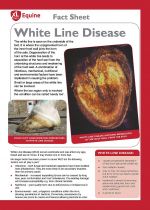
White Line Disease
The white line is seen on the underside of the foot. It is where the unpigmented horn of the inner hoof wall joins the horn of the sole.